Get your tickets to THE BIG THING 2026!
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Eliminating DEF from a FUSO
- Thread starter pdx2ptg
- Start date
There was a thread on this site where someone here in the USA attempted to use their DPF delete kit. The result was a lighter wallet and utter frustration. I recall they had to uninstall everything.
Last edited:
Here's the thread regarding Chiptuning's DPF delete effort on a USA Fuso;
http://www.expeditionportal.com/forum/threads/125495-chiptune-dpf-delete-problems?highlight=DPF
http://www.expeditionportal.com/forum/threads/125495-chiptune-dpf-delete-problems?highlight=DPF
mog
Kodiak Buckaroo
The problem with the Fuso is very little support (AKA no profitable market via vehicle quantity or $$ in enthusiast's wallets) so even tuning chips are not available in the US.Not entirely true. I imagine you would have said that about a 2009 BMW X5 35d as well. Yet I have a kit coming with a new downpipe to replace the SCR/DPF; simultaneously pull the ECU for reprogramming with a particular specialist; voila, no fuel consuming/CO2 increasing regenerations with no CE lights. For the Fuso, someone who knows how (understands the ECU) just needs to do it.
Please spare the political diatribes.
Charlie
We would all love to have the same options that the US trucks and various sports cars from all nations have, but as yet, nothing promising.
Not a DEF guy here. But with the reported 300-400 miles per gallon, it sounds like a 5 gallon container would give you an extra 1500-2000 miles past what the Fuso holds now (3 gallons so 900-1200 miles?), so a total non-resupplied range of 2400 to 3200 miles should do it ??
Mr Rehab
Traveller
Likewise thanks dlh62c for the 2015 Diesel Sulphur map - I used the same source when we were planning our 2013 trip through Asia.
I have a 2010 Euro IV Isuzu NPS (Australian model) which was fitted with DPD but no DEF. The outlook was similarly worrying as in the 2012 map below, plus some countries like Malaysia and Kazakhstan hadn't progressed as planned and the map optimistic, however the reality on the ground wasn't quite so bad. LSD diesel (10 to 50ppm) was available in some towns in Lao, China and Mongolia and 350ppm available most everywhere else. The Isuzu ran fine on 350ppm with no excess smoke and no increase in regen rate - not saying it wouldn't shorten the life of the filter but it certainly didn't cause any problems enroute, and filters can be cleaned. So, my point is that it would be useful to know what exactly is on sale at the bowser rather than what's allowable under national regs. Is it possible to get feedback from overlanders who've recently been in Sth America?
What ended up being more restrictive with the Isuzu was that the truck wouldn't complete a regen above 2000m, and we met some German overlanders in Mongolia with the same problem with their pick-up. This would have to limit route options for Sth America. Do the more recent DPD/DEF equipped Fuso and Isuzu cope with higher altitudes?
Earlier this year I finally had the DPD removed, EGR disabled and power boosted by 20% courtesy of an Austrian engine tuner. We do have one check light on the dash but overall...YIPPPEE!!!!

I have a 2010 Euro IV Isuzu NPS (Australian model) which was fitted with DPD but no DEF. The outlook was similarly worrying as in the 2012 map below, plus some countries like Malaysia and Kazakhstan hadn't progressed as planned and the map optimistic, however the reality on the ground wasn't quite so bad. LSD diesel (10 to 50ppm) was available in some towns in Lao, China and Mongolia and 350ppm available most everywhere else. The Isuzu ran fine on 350ppm with no excess smoke and no increase in regen rate - not saying it wouldn't shorten the life of the filter but it certainly didn't cause any problems enroute, and filters can be cleaned. So, my point is that it would be useful to know what exactly is on sale at the bowser rather than what's allowable under national regs. Is it possible to get feedback from overlanders who've recently been in Sth America?
What ended up being more restrictive with the Isuzu was that the truck wouldn't complete a regen above 2000m, and we met some German overlanders in Mongolia with the same problem with their pick-up. This would have to limit route options for Sth America. Do the more recent DPD/DEF equipped Fuso and Isuzu cope with higher altitudes?
Earlier this year I finally had the DPD removed, EGR disabled and power boosted by 20% courtesy of an Austrian engine tuner. We do have one check light on the dash but overall...YIPPPEE!!!!

Last edited:
charlieaarons
Explorer
Likewise thanks dlh62c for the 2015 Diesel Sulphur map - I used the same source when we were planning our 2013 trip through Asia.
I have a 2010 Euro IV Isuzu NPS (Australian model) which was fitted with DPD but no DEF. The outlook was similarly worrying as in the 2012 map below, plus some countries like Malaysia and Kazakhstan hadn't progressed as planned and the map optimistic, however the reality on the ground wasn't quite so bad. LSD diesel (10 to 50ppm) was available in some towns in Lao, China and Mongolia and 350ppm available most everywhere else. The Isuzu ran fine on 350ppm with no excess smoke and no increase in regen rate - not saying it wouldn't shorten the life of the filter but it certainly didn't cause any problems enroute, and filters can be cleaned. So, my point is that it would be useful to know what exactly is on sale at the bowser rather than what's allowable under national regs. Is it possible to get feedback from overlanders who've recently been in Sth America?
What ended up being more restrictive with the Isuzu was that the truck wouldn't complete a regen above 2000m, and we met some German overlanders in Mongolia with the same problem with their pick-up. This would have to limit route options for Sth America. Do the more recent DPD/DEF equipped Fuso and Isuzu cope with higher altitudes?
Earlier this year I finally had the DPD removed, EGR disabled and power boosted by 20% courtesy of an Austrian engine tuner. We do have one check light on the dash but overall...YIPPPEE!!!!
View attachment 302544
Once again the confusion hits. first of all, I would guess "DPD" = "diesel particulate device" = DPF ="diesel particulate filter" ?? A DPF = DPD isn't affected by sulfur content! The main thing that clogs it up is high ash lube oil combustion products (Ca and Mg oxides). High ash oil is incidentally desirable when burning high sulfur diesel to counteract acid buildup in the sump. OTOH high sulfur in the fuel and high phosphorus in the oil DOES wreck the SCR (selective catalyst reduction), which uses DEF (diesel exhaust fluid) - urea - to make ammonia to reduce NOx.
So - for overland travel - why delete SCR/DEF? High sulfur fuel will gradually destroy system and cause all sorts of maladies like limp mode, check engine lights, etc etc. AND lack of availability of DEF.
Why delete DPF? Stop fuel consuming regenerations, get 20-25% better mileage; secondarily able to use high alkalinity lube oil and avoid very frequent oil changes with high sulfur diesel. Also evidently the altitude limitation will go away.
And finally, why delete EGR? If it leaks coolant into the intake (a VERY common failure mode) and then into sump, coolant can wreck bearings; EGR valve often fails; parts not available in 3rd world; EGR frequently gums up turbo compressor side; EGR screws up lube oil. I have had EGR failures on both my Unimog and BMW.
There is nothing inherently bad for the engine internals about high sulfur diesel except for the acid issue, which can be mitigated with the proper lube oil (only if DPF/SCR is gone). In fact injection systems "like" HSD (better lubrication). Any traveller who blames injection system failures on HSD is full of hooey. What causes these failures is water and/or dirt in the fuel, which isn't rare in certain locales.
Mr Rehab, how much did mpg change with DPD = DPF removal?
Charlie
Last edited:
GR8ADV
Explorer
Once again the confusion hits. first of all, I would guess "DPD" = "diesel particulate device" = DPF ="diesel particulate filter" ?? A DPF = DPD isn't affected by sulfur content! The main thing that clogs it up is high ash lube oil combustion products (Ca and Mg oxides). High ash oil is incidentally desirable when burning high sulfur diesel to counteract acid buildup in the sump. OTOH high sulfur in the fuel and high phosphorus in the oil DOES wreck the SCR (selective catalyst reduction), which uses DEF (diesel exhaust fluid) - urea - to make ammonia to reduce NOx.
So - for overland travel - why delete SCR/DEF? High sulfur fuel will gradually destroy system and cause all sorts of maladies like limp mode, check engine lights, etc etc. AND lack of availability of DEF.
Why delete DPF? Stop fuel consuming regenerations, get 20-25% better mileage; secondarily able to use high alkalinity lube oil and avoid very frequent oil changes with high sulfur diesel. Also evidently the altitude limitation will go away.
And finally, why delete EGR? If it leaks coolant into the intake (a VERY common failure mode) and then into sump, coolant can wreck bearings; EGR valve often fails; parts not available in 3rd world; EGR frequently gums up turbo compressor side; EGR screws up lube oil. I have had EGR failures on both my Unimog and BMW.
There is nothing inherently bad for the engine internals about high sulfur diesel except for the acid issue, which can be mitigated with the proper lube oil (only if DPF/SCR is gone). In fact injection systems "like" HSD (better lubrication). Any traveller who blames HSD on injection system failures is full of hooey. What causes these failures is water and/or dirt in the fuel, which isn't rare in certain locales.
Mr Rehab, how much did mpg change with DPD = DPF removal?
Charlie
Wow. Clearly happy with my 2004.
Isuzu calls their diesel particulate filter a DPD, short for Diesel Particulate Diffuser.
https://www.osha.gov/dts/hazardalerts/diesel_exhaust_hazard_alert.html
https://www.osha.gov/dts/hazardalerts/diesel_exhaust_hazard_alert.html
Last edited:
Mr Rehab
Traveller
DPD=DPF
" Once again the confusion hits. first of all, I would guess "DPD" = "diesel particulate device" = DPF ="diesel particulate filter" ?? A DPF = DPD isn't affected by sulfur content!"
Now I am confused. The Isuzu DPD=DPF system uses an oxidation catalyst in front of a wall-flow filter. My layman understanding was that HS diesel reduces the effectiveness of the catalyst which reduces the effectiveness of the regen process and leads to excess PM which is picked up in the filter. HS diesel reduces temperatures reached in the regen cycle which reduces the ability of the system to clean out the filter and will shorten system life. So a DPF system needs ULSD, yes or maybe no?
The sources below are clear that a DPF needs ULSD but that might depend on the type of filter used - the Isuzu uses a wall flow filter but if you wade through the cut and paste info below you'll find mention of a Flow Through Particulate Matter Filter. This filter type won't be blocked by use of HS diesel but will have efficiency degraded. No idea if that efficiency degradation will be identified by the ECU and cause problems. Perhaps this is the type of DPF you are referring to Charlie?
A/ This from a UNEP Report from around 2009 Cleaner Vehicles: The Role of Lower Sulphur Fuels
“4.1 How Sulphur in Fuel Affects Vehicle Emissions: The Systems Approach
Reducing sulphur levels in fuels is especially important in reducing the smallest particles
and can reduce vehicle emissions in two ways:
First, reducing sulphur in fuels reduces direct emissions of both sulphur dioxide and
sulphate PM from all vehicles, old and new.24 Sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions from diesel
and petrol vehicles and particulate matter from diesel vehicles tend to increase in direct
proportion to the amount of sulphur in the fuel. While sulphate particles may account for
only a small fraction of particle volume or mass, they are fine and ultra-fine in particle size
and account for a large fraction of particle numbers.25
Second, sulphur poisons or reduces the effectiveness of vehicle emission control
technologies for petrol and diesel vehicles, resulting in increased vehicle emissions of carbon
monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon (HC), nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter (PM). It
also poisons or reduces the effectiveness of new types of emission control devices such as
advanced catalytic converters and diesel particle traps, which can further reduce NOx, HC,
and PM emissions.”
“However, sulphur greatly reduces their efficiency. When a DOC oxidizes sulphur, the
resulting sulphate PM collects on the filter. This reduces its efficiency, which increases emissions,
and increases the need for regeneration, which reduces the vehicle's fuel economy.
High levels of sulphur can render the DPF ineffective or even stop the engine due to unacceptable
backpressure. DPFs should not be used with fuel sulphur levels greater than 50ppm.”
B/ These slides from a NATO investigation into Fuel Compatibility with Euro IV Engines. Note the reference to sulphated ash or products of other ash forming components eg engine oil additives.
I wasn't planning on using the Isuzu for military purposes but you never know…..


C/ From another NATO report into problems related to HS Diesel on emission technology.
2.2.2.1 Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOCs)
It has been identified that high sulphur reduces the efficiency of the catalyst by reducing its
operating temperature and by increasing the formation of sulphated ash. The low operating temperature of
the oxidation catalyst reduces the formation of NO2 needed for the regeneration of the DPF.
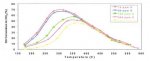
2.2.2.2 Fuel Sulphur Effects on Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF).
HSF will cause two different types of negative effects. The first will reduce the catalyst efficiency by
reducing the high operating temperature needed for regenerating the DPF. The second one will be
caused by the oxidation of sulphur dioxide resulting in high levels of sulphated ash and total particulate mass.
Depending on the DPF design the experienced negative effects will differ as follows:
1) Fuel Sulphur Effects on Wall Flow Diesel Particulate Filter (WF-DPF)
The WF-DPF is a honey comb structure with parallel pipes. These pipes are alternating closed and
opened. The inlet pipe at one end and the outlet pipe at the other. Thus gas may only flow through the
wall of the filter. Soot particles will be collected in the inlet pipe.
Using HSF will result in an increased loading of the filter and causing frequent regenerating cycles.
Additionally, to the reduced performance of the oxidation catalyst will result in an overload and a blocking of the filter. The filter must then be replaced or regenerated externally.
2) Fuel Sulphur Effects on Flow-Through Metallic Particulate Matter Filter (M-PMF)
M-PMF is structured in a layered stack consisting of corrugation foil with shovels and porous fleece.
Exhaust gas is introduced to both up and down side of fleeces by shovels, and then soot is trapped while gaseous components pass the fleece. The nitrogen oxides produced in the oxidation pre-catalyst
cause the soot particles to be burned continuously.
As explained in Annex A, the use of HSF will reduce the overall efficiency of the system but will not block the M-PMF.
Fuel consumption/MPG? The truck was using 16-17L/100km (14.7 US mpg) before the change and 16L/100km after the changes. I was happy to see consumption basically unchanged but with a 20% power boost which I assumed would need more fuel.
" Once again the confusion hits. first of all, I would guess "DPD" = "diesel particulate device" = DPF ="diesel particulate filter" ?? A DPF = DPD isn't affected by sulfur content!"
Now I am confused. The Isuzu DPD=DPF system uses an oxidation catalyst in front of a wall-flow filter. My layman understanding was that HS diesel reduces the effectiveness of the catalyst which reduces the effectiveness of the regen process and leads to excess PM which is picked up in the filter. HS diesel reduces temperatures reached in the regen cycle which reduces the ability of the system to clean out the filter and will shorten system life. So a DPF system needs ULSD, yes or maybe no?
The sources below are clear that a DPF needs ULSD but that might depend on the type of filter used - the Isuzu uses a wall flow filter but if you wade through the cut and paste info below you'll find mention of a Flow Through Particulate Matter Filter. This filter type won't be blocked by use of HS diesel but will have efficiency degraded. No idea if that efficiency degradation will be identified by the ECU and cause problems. Perhaps this is the type of DPF you are referring to Charlie?
A/ This from a UNEP Report from around 2009 Cleaner Vehicles: The Role of Lower Sulphur Fuels
“4.1 How Sulphur in Fuel Affects Vehicle Emissions: The Systems Approach
Reducing sulphur levels in fuels is especially important in reducing the smallest particles
and can reduce vehicle emissions in two ways:
First, reducing sulphur in fuels reduces direct emissions of both sulphur dioxide and
sulphate PM from all vehicles, old and new.24 Sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions from diesel
and petrol vehicles and particulate matter from diesel vehicles tend to increase in direct
proportion to the amount of sulphur in the fuel. While sulphate particles may account for
only a small fraction of particle volume or mass, they are fine and ultra-fine in particle size
and account for a large fraction of particle numbers.25
Second, sulphur poisons or reduces the effectiveness of vehicle emission control
technologies for petrol and diesel vehicles, resulting in increased vehicle emissions of carbon
monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon (HC), nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter (PM). It
also poisons or reduces the effectiveness of new types of emission control devices such as
advanced catalytic converters and diesel particle traps, which can further reduce NOx, HC,
and PM emissions.”
“However, sulphur greatly reduces their efficiency. When a DOC oxidizes sulphur, the
resulting sulphate PM collects on the filter. This reduces its efficiency, which increases emissions,
and increases the need for regeneration, which reduces the vehicle's fuel economy.
High levels of sulphur can render the DPF ineffective or even stop the engine due to unacceptable
backpressure. DPFs should not be used with fuel sulphur levels greater than 50ppm.”
B/ These slides from a NATO investigation into Fuel Compatibility with Euro IV Engines. Note the reference to sulphated ash or products of other ash forming components eg engine oil additives.
I wasn't planning on using the Isuzu for military purposes but you never know…..


C/ From another NATO report into problems related to HS Diesel on emission technology.
2.2.2.1 Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOCs)
It has been identified that high sulphur reduces the efficiency of the catalyst by reducing its
operating temperature and by increasing the formation of sulphated ash. The low operating temperature of
the oxidation catalyst reduces the formation of NO2 needed for the regeneration of the DPF.

2.2.2.2 Fuel Sulphur Effects on Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF).
HSF will cause two different types of negative effects. The first will reduce the catalyst efficiency by
reducing the high operating temperature needed for regenerating the DPF. The second one will be
caused by the oxidation of sulphur dioxide resulting in high levels of sulphated ash and total particulate mass.
Depending on the DPF design the experienced negative effects will differ as follows:
1) Fuel Sulphur Effects on Wall Flow Diesel Particulate Filter (WF-DPF)
The WF-DPF is a honey comb structure with parallel pipes. These pipes are alternating closed and
opened. The inlet pipe at one end and the outlet pipe at the other. Thus gas may only flow through the
wall of the filter. Soot particles will be collected in the inlet pipe.
Using HSF will result in an increased loading of the filter and causing frequent regenerating cycles.
Additionally, to the reduced performance of the oxidation catalyst will result in an overload and a blocking of the filter. The filter must then be replaced or regenerated externally.
2) Fuel Sulphur Effects on Flow-Through Metallic Particulate Matter Filter (M-PMF)
M-PMF is structured in a layered stack consisting of corrugation foil with shovels and porous fleece.
Exhaust gas is introduced to both up and down side of fleeces by shovels, and then soot is trapped while gaseous components pass the fleece. The nitrogen oxides produced in the oxidation pre-catalyst
cause the soot particles to be burned continuously.
As explained in Annex A, the use of HSF will reduce the overall efficiency of the system but will not block the M-PMF.
Fuel consumption/MPG? The truck was using 16-17L/100km (14.7 US mpg) before the change and 16L/100km after the changes. I was happy to see consumption basically unchanged but with a 20% power boost which I assumed would need more fuel.
Last edited:
Mr Rehab
Traveller
Isuzu calls their diesel particulate filter a DPD, short for Diesel Particulate Diffuser.
https://www.osha.gov/dts/hazardalerts/diesel_exhaust_hazard_alert.html
Hazard Alert on diesel PM? The Isuzu will still be cleaner than the trucks in those countries where you’ll be buying HS diesel and cleaner than the other Overlanders option of driving a vehicle from the 80s or 90s, desirable as that may be for other reasons.
charlieaarons
Explorer
I guess I was (partially) confused. I guessed that your DPD was just a DPF. It appears there is a catalyst also, but not a reduction catalyst; just oxidation, for mainly soot and also (low in diesels) CO. Yes, you are correct, sulfur poisons your catalyst. It also appears that sulfur, especially when combined with high ash lube oil and some degree of lube oil consumption, will increase metallic sulfated ash deposits and soot in the DPF - especially when the catalyst (a source of heat to burn things like soot) is poisoned by HSD.
The metal content of diesel fuel itself, whether HSD or LSD, is supposed to be very low.
Charlie
The metal content of diesel fuel itself, whether HSD or LSD, is supposed to be very low.
Charlie
Similar threads
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 30
- Views
- 8K
- Replies
- 35
- Views
- 10K
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 4K
